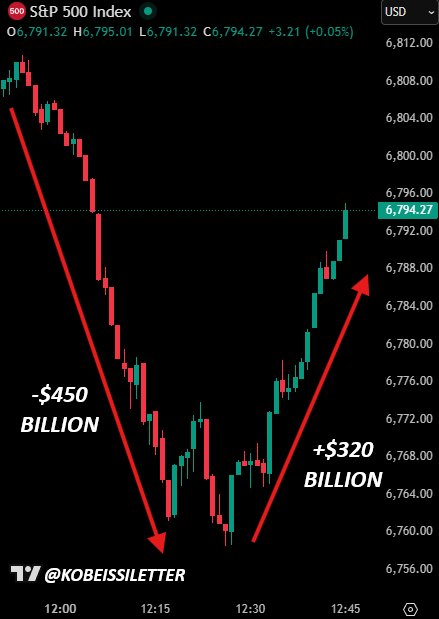
Markets Rally Amid Historic Swing: S&P 500 Rebounds After $720 Billion Intrahour Move
A dramatic intraday swing rattled U.S. stock markets today as the S&P 500 endured a rapid, high-volatility session that flashed across trading screens, prompting widespread discussion among investors, economists, and policymakers. Between 11:55 AM and 12:25 PM ET, the broad index suffered a $450 billion decline in market capitalization, only to rebound with $320 billion of that loss erased by 12:48 PM. In total, the session logged a $720 billion swing in under an hour, underscoring the volatile dynamics that have become increasingly common in contemporary equity markets.
Historical context: a teaching moment for volatility The day’s price action arrives amid a longer arc of market turbulence, though the scale of the move was uncommon even in recent years characterized by elevated volatility. Market historians note that intraday swings of this magnitude echo episodes from the past when liquidity conditions tightened, program trading accelerated, ors triggered rapid shifts in risk sentiment. In those moments, the price discovery process becomes intensely reflexive: traders scramble to reassess fundamentals, bid-ask spreads widen, and computerized trading strategies amplify price moves before participants reestablish equilibrium.
While no single factor supplies a complete explanation, several elements converged in the hours around the swing. First, real-time data indicated a sudden recalibration of expectations for interest rates and inflation, with investors pricing in potential shifts in central bank policy paths. Second, sector rotation intensified as investors moved quickly between cyclicals and defensives, amplifying moves in both directions. Third, a burst of program-driven activity—algorithms designed to execute large orders across multiple venues—appeared to amplify price dislocations before liquidity providers stepped in to restore balance. Together, these components produced a volatile, high-volume trading environment that culminated in a rapid loss and subsequent partial recovery.
Economic impact: effects reverberate beyond the tape Though the move was primarily captured in market capitalization and index levels, the broader economic implications are being analyzed by researchers and market participants. A one-hour swing of this magnitude can influence short-term confidence among household and institutional investors, affect funding costs for leveraged strategies, and alter perceived risk premia across asset classes. For corporate executives, the intraday volatility can complicate financial planning, particularly for businesses with hedging programs tied to index levels or volatility-sensitive instruments.
From a macro perspective, episodes of heightened intraday volatility often prompt closer scrutiny of liquidity dynamics in underlying markets. When liquidity thinness coincides with rapid price declines, market participants may face wider bid-ask spreads and greater slippage on trades, potentially increasing trading costs and dampening real economic activity in the near term. On the other hand, strong intraday reversals can restore market confidence, signaling that buyers are ready to step in and reassert a floor of demand even in uncertain environments.
Regional comparisons: how other markets fared on the same day The United States focus of the day’s swing drew attention from global market watchers, but similar episodes have occurred in other major markets under comparable conditions. In recent years, equity markets in Europe and Asia-Pacific have experienced parallel bursts of volatility tied to global growth signals, commodity price movements, and shifts in monetary policy expectations. Analysts note that while the pace and magnitude of intraday moves can differ due to market structure, trading hours overlap, and currency dynamics, the underlying drivers—liquidity, risk appetite, and macro news flow—tend to align across regions during periods of heightened uncertainty.
In Europe, for example, major stock indices often exhibit synchronised moves with U.S. sentiment during sessions with key economic data releases or central bank communication. Across Asia-Pacific, markets can respond more acutely to commodity price fluctuations and regional geopolitical developments, reflecting different exposure profiles and hedging needs. The day’s events thus add to a growing body of evidence that, in a tightly integrated global financial system, a shock in one major market can propagate quickly to others, even as local conditions modulate the transmission.
Market structure factors: liquidity, liquidity provision, and price discovery Experts emphasize that structural elements of the market contributed to the day’s volatility. Liquidity—the ease with which assets can be bought or sold without moving the price—tends to thin during certain trading conditions, particularly in the midday trough that accompanies lunch-hour liquidity gaps in some time zones. The presence and behavior of market makers and high-frequency traders can magnify effects when they recalibrate risk limits in response to shifting prices, especially if automated strategies are triggered by rapid moves in underlying benchmarks.
Regulators and market participants often scrutinize such episodes to assess whether current safeguards—like circuit breakers, tradable quotation requirements, and transparency measures—adequately mitigate disorderly price action. While no policy change is announced in the immediate aftermath of a single day’s swing, the episode is likely to feed into ongoing debates about how best to balance liquidity provision with the risk of fragility in fast-moving markets.
Investor reaction: risk sentiment, hedging activity, and flow patterns For individual and institutional investors, the intraday volatility tested risk controls and highlighted the importance of disciplined portfolio management. Some traders reported reallocating exposure in real time, preferring to reduce tilt toward highly correlated equities and cyclicals during the peak volatility window. Others sought hedges using options and volatility instruments, trying to protect against further downside while remaining prepared to participate in any sustained rebound.
Public sentiment reflected a mix of concern and opportunity. In hours of stress, some market participants emphasized the importance of diversification and long-horizon planning, while others pointed to the potential for mispricing and the chance to add selectively to high-quality names at apparent discounts. The dynamic underscored why many investors emphasize a disciplined approach to risk management, including predefined stop-loss rules, robust diversification, and careful monitoring of liquidity risk.
Sectors and standout movers: who led and who lagged Throughout the session, sector performance was uneven, with some areas experiencing sharper downdrafts while others held up more robustly. Financials and technology often attract heightened attention during high-volatility periods due to their sensitivity to interest rate expectations and earnings visibility. Energy, utilities, and consumer staples sometimes exhibit relative resilience when risk appetite shifts abruptly, given their traditional characteristics as defensive or value-oriented holdings. In today’s episode, the precise sector-by-sector movement reflected a complex interplay of macro signals, earnings outlooks, and evolving investor preferences.
Volatility metrics: measuring the turbulence Volatility indices, futures, and option-implied measures typically respond to intraday swings as traders price in changing risk expectations. In the wake of the day’s activity, markets will likely see elevated readings on short-term volatility gauges, which can influence the cost of hedging and the attractiveness of riskier assets for a period after the event. Analysts often track the VIX as a snapshot of collective anxiety, though it is not a perfect predictor of near-term returns. The interplay between realized volatility and implied volatility offers clues about whether traders view the move as an overreaction or an opportunity for reallocation.
What comes next: outlook for investors and policymakers Looking ahead, investors will reassess positioning in light of the intraday swing. Many market participants expect a period of consolidation as markets attempt to digest the day’s price action, reassess earnings trajectories, and weigh ongoing macro risks such as inflation trajectories, geopolitical developments, and policy expectations. Confidence may hinge on incoming economic data, corporate earnings results, and any signals from central banks regarding inflation and growth prospects.
From a policymaking perspective, the episode is likely to prompt closer scrutiny of market integrity mechanisms and liquidity strategies. Regulators may seek input from market participants on how best to balance rapid price discovery with the need to maintain orderly markets during periods of stress. While policy shifts are not automatic in response to a single day’s swing, the event will contribute to ongoing dialogues about market architecture, transparency, and resilience.
Public reaction: how communities viewed the day’s swings Public interest in the intraday movement reflected broader concerns about the health of the economy and the stability of financial markets. Newsrooms, educational institutions, and financial advisory services reported heightened demand for explanations about market mechanics and risk management. In communities where investment accounts play a significant role, residents watched the ticker with a mix of caution and curiosity, seeking to understand what such moves might mean for retirement plans, college savings, and personal portfolios.
Regional economic ripple effects: if any While the immediate impact was financial, broader regional effects are possible over time as market confidence interacts with consumer spending, business investment, and bank lending appetite. A sustained period of volatility can influence corporate financing costs, which in turn can affect capital expenditures and hiring plans. Regional markets with heavy exposure to sectors affected by the move may experience more pronounced reactions in trade, investment, and employment indicators, though the direct causality would depend on subsequent data and policy responses.
Historical benchmarks: comparing to notable intraday events Historically, intraday swings of this magnitude are uncommon but not unprecedented. Market observers will likely compare today’s episode to past instances when liquidity strains and macro news converged to spark rapid price moves followed by reversals. Each episode offers a learning opportunity for traders, institutions, and regulators to refine strategies for risk management, trading protocols, and market-wide safeguards that protect participants without constraining legitimate price discovery.
Closing perspective: a moment in a longer story Today’s intraday surge and retracement add to the ongoing narrative of a modern, highly interconnected financial system where information travels quickly, and liquidity can shift in an instant. As market participants absorb the day’s lessons, the focus remains on disciplined risk management, informed decision-making, and robust market infrastructure that can withstand pressure while continuing to enable effective price discovery for investors of all sizes. The episode serves as a reminder that in financial markets, vigilance, resilience, and clarity about one’s long-term investment goals are essential amid ever-present uncertainty.
Follow-up note This article provides a detailed, context-rich account of the intraday market swing, incorporating historical context, economic implications, and regional comparisons without political commentary.