)
China Leads Historic Shift in Global Auto Industry as 2025 Sales Signal New Era
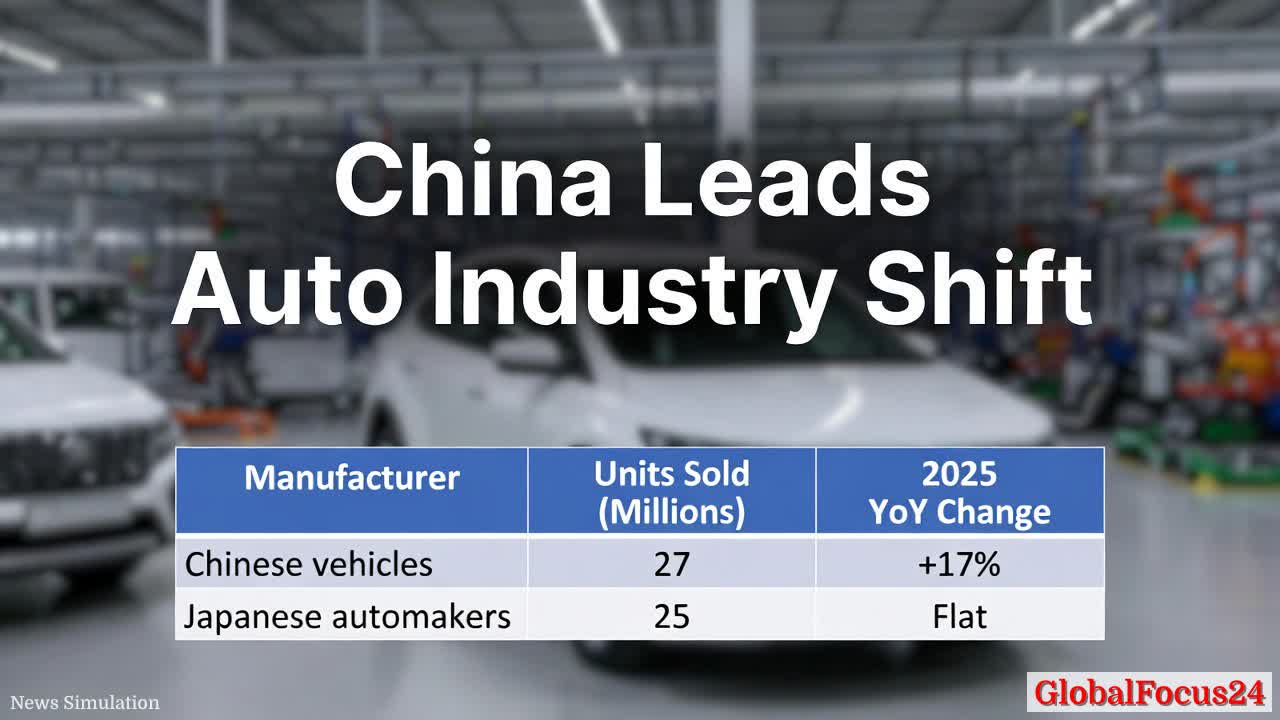
The global auto sector is undergoing a seismic shift, with China driving a historic reordering of market leadership that could redefine competition, supply chains, and regional economic dynamics for years to come. Early-year indicators and industry estimates point to a robust surge in Chinese vehicle sales in 2025, achieving a year-over-year increase of about 17% to roughly 27 million units. That ascent not only marks a new record for China but also signals a broad realignment in the balance of power among the world’s leading automakers, with implications for production hubs, technology development, and consumer preferences across continents.
Historical context: a long arc toward market leadership
China’s ascent in the automotive industry is the culmination of a multi-decade trajectory rooted in policy incentives, manufacturing scale, and a rapid adoption of new technologies. Since the early 2000s, Chinese automakers and joint ventures have invested heavily in electrification, connected-car capabilities, and domestic supply chains. The government’s supportive policies—ranging from generous subsidies for EVs to mandates for new-energy vehicle (NEV) adoption—helped build a domestic ecosystem capable of competing with established global brands. By the 2010s, China had already emerged as the world’s largest producer of vehicles in many years, but the 2025 data suggests a shift from sheer manufacturing volume toward a leadership stance, particularly in the fast-growing electric and hybrid segments.
Economic impact: spillovers beyond the showroom floor
The surge in Chinese auto sales injects momentum into the broader economy through several channels. First, higher domestic demand translates into increased production at domestic factories, which supports jobs, raises wage levels in manufacturing regions, and strengthens supplier networks that feed into a wide range of industries from battery materials to autonomous software. Second, as China expands its role in the global supply chain, foreign partners may recalibrate sourcing to align with Chinese platforms, batteries, and vehicle architectures. This could influence commodity markets—especially lithium, cobalt, nickel, and rare earth elements—alongside the regional logistics landscape as ports, rail, and trucking networks adapt to higher output.
Additionally, the international competitiveness of Chinese automakers is enhancing cross-border consumer options. As brands from China push into overseas markets, the cost structures that once favored established players are challenged by economies of scale and aggressive pricing. This could pressure traditional automakers to accelerate product modernization, battery technology improvements, and software-driven features to sustain margins. The broader technology ecosystem around mobility—ranging from charging infrastructure to connected services and after-sales support—stands to gain from intensified competition and collaborative opportunities across Asia, Europe, and the Americas.
Regional comparisons: where China stands today
- Asia-Pacific: China’s domestic gains amplify its regional influence, particularly as neighboring economies grapple with supply chain diversification. Regional automakers are watching closely to see if Chinese platforms gain traction in markets such as Southeast Asia, where growth in mobility demand is robust and consumer preferences are evolving toward practical, affordable EVs.
- Europe: European automakers have long competed on engineering excellence, branding, and regulatory adaptation. Chinese OEMs expanding into Europe bring price competitiveness and a broad product lineup, including electric crossovers and compact vehicles tailored to urban environments. European suppliers are increasingly integrating with Chinese production networks, reshaping the continent’s manufacturing rhythms and investment priorities.
- North America: The United States and Canada face a shifting landscape as Chinese brands explore market access and local partnerships. The implications for U.S. manufacturing policy, trade relations, and battery supply chains are complex, involving considerations of national security, critical minerals, and the evolving incentives for domestic EV production.
Technological edge: the race in electrification and software
A critical driver of China’s rising sales is the rapid deployment of electric vehicles and advanced smart features. Domestic battery makers, including several scale-focused producers, have scaled to meet growing demand, contributing to lower costs and improved charging performance. Chinese automakers have also invested heavily in software-defined vehicles, enabling over-the-air updates, sophisticated driver-assistance systems, and integrative ecosystems that tie vehicles to digital services. This convergence of hardware and software is reshaping what customers expect from a car, turning mobility into a platform for data, entertainment, and on-demand services.
Regulatory landscape and consumer confidence
Policy oversight remains a double-edged sword for the industry. On one hand, supportive policies have driven adoption, accelerated charging infrastructure deployment, and catalyzed innovation in battery technology. On the other hand, regulatory scrutiny—particularly around safety standards, data privacy, and trade practices—requires manufacturers to maintain rigorous compliance across multiple markets. Consumer confidence in vehicle safety, reliability, and after-sales service remains a foundational component of sustained growth. The 2025 sales trajectory implies that Chinese automotive brands have built reputations for value, durability, and evolving feature sets that resonate with a broad consumer base.
Supply chain resilience and geopolitical considerations
The 2025 data underlines the importance of resilient supply chains for a high-volume, technology-intensive industry. Semiconductor availability, battery materials, and software components must be reliably sourced to sustain growth. China’s expanding role in the supply chain also elevates the importance of regional diversification—a lesson many automakers are absorbing as they navigate tariffs, export controls, and cross-border logistics. As automakers seek to optimize costs and reliability, partnerships with upstream suppliers, joint ventures, and regional production footprints will be key strategies to manage risk while pursuing scale.
Public reaction and market sentiment
Public reaction to China’s growing dominance in the auto sector has been mixed, reflecting a mix of admiration for affordability and technology, alongside concerns about market competition and employment in traditional automotive hubs. In many regions, consumers are benefiting from wider choices and improved features at competitive prices. At the same time, industry stakeholders—dealers, technicians, and supply chain workers—are adapting to a faster pace of change, including the integration of electrification and connected-car services into standard product offerings. The narrative around China’s automotive ascent is increasingly one of transformation and opportunity rather than disruption, emphasizing how the industry is evolving in a global context.
Looking ahead: what the numbers imply for 2026 and beyond
The 2025 sales milestone sets the stage for continued momentum into 2026. If the current trajectory holds, the market could see sustained gains in Chinese vehicle production and exports, with domestic demand continuing to expand as urbanization and middle-class growth persist. International markets may experience increased competition as Chinese brands push into new regions, demanding more from infrastructure, service networks, and regulatory alignment. Economists and industry analysts will be watching for indicators such as per-vehicle profitability, after-sales revenue growth, and the rate at which battery costs decline, all of which influence the long-term sustainability of the growth story.
Environmental and social implications
The industry’s shift toward electrification aligns with broader environmental goals and national commitments to reduce emissions from transportation. As more vehicles on the road are battery-powered, charging infrastructure and grid readiness become increasingly critical. The pace of adoption also raises questions about battery lifecycle management, recycling capabilities, and the environmental footprint of raw material extraction. Policymakers and industry players will need to continue collaborating to balance the benefits of rapid electrification with responsible resource management and social considerations, ensuring that the transition supports both climate goals and equitable access to mobility.
Conclusion: a pivotal moment for global mobility
China’s leadership in the global auto industry marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of mobility. The 2025 performance illustrates a convergence of scale, technology, and consumer demand that is redefining what is possible in vehicle design, manufacturing, and service ecosystems. As automakers around the world respond to these shifts, the industry can anticipate intensified competition, accelerated innovation, and a broader set of choices for drivers everywhere. The coming years will reveal whether this momentum translates into sustained market leadership, or whether new developments—such as breakthroughs in energy storage, autonomous driving, or regulation—will shape a more complex, multi-polar automotive landscape.