Rapid Decline in DEX Execution Costs Outpaces Centralized Exchanges
A profound shift is reshaping crypto markets as decentralized exchanges (DEXs) deliver execution costs that rival, and in some cases surpass, those of traditional centralized platforms. This transformation is redefining how institutions and sophisticated traders approach digital asset markets, signaling a new era where on-chain trading competes on speed, efficiency, and cost with legacy venues.
Historical context: from off-chain liquidity to on-chain efficiency For years, the dominant model in crypto liquidity involved off-chain arrangements hosted by centralized exchanges. Traders relied on order books and liquidity pools maintained by entities such as Coinbase and Binance, with large-ticket trades often incurring significant price impact and liquidity risk. The centralized model benefited from deep liquidity, high throughput, and extensive infrastructure, but it also carried counterparty risk, regulatory uncertainty, and reliance on a single venue or few venues for large executions.
The emergence of decentralized exchanges began addressing these concerns by bringing trade settlement onto public blockchains. Early AMMs (automated market makers) on chains like Solana and Ethereum offered permissionless access, transparent pricing, and settlement finality anchored in the underlying chain. Yet early iterations faced challenges: higher slippage for large trades, route inefficiencies across multiple pools, and fragmentation of liquidity across networks. Over time, technological innovations in on-chain order routing, cross-chain bridges, and concentrated liquidity has led to meaningful reductions in execution costs for sizable trades.
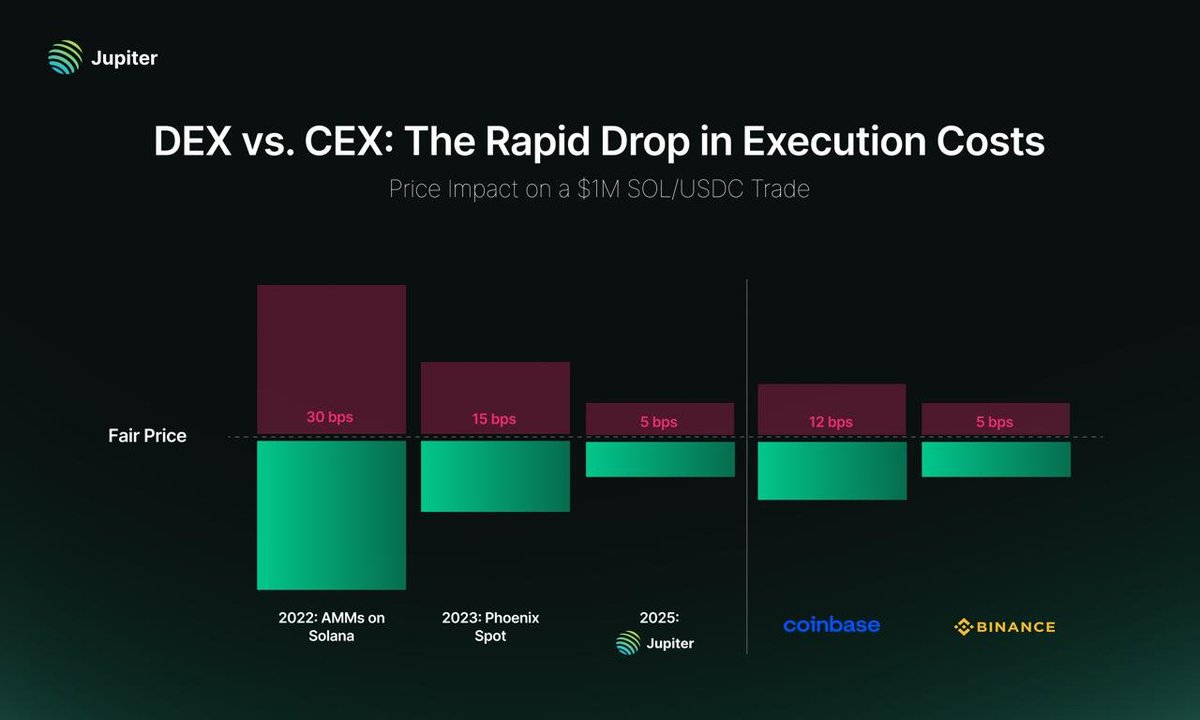
Recent data highlight a sharp improvement in on-chain execution quality A recent analysis demonstrates that executing a $1 million SOL/USDC trade on Solana-based DEXs can achieve a price impact as low as 5 basis points. This marks a striking improvement from 2022, when automated market makers on Solana could produce around 30 basis points of price impact for comparable trades, and from 2023, when Phoenix Spot reported roughly 15 basis points for large Solana trades. In contrast, traditional centralized venues show different profiles: executing the same trade on Coinbase can produce around 12 basis points of price impact, while Binance—one of the largest centralized exchanges by liquidity—aligns with the 5 basis point level observed on the best-performing DEXs in this analysis.
These numbers are more than a snapshot; they illustrate a structural trend. On-chain execution quality has reached a level where large, institution-grade orders can be routed with low slippage without leaving the security and transparency of a public blockchain. The convergence of on-chain technology, concentrated liquidity provision, and advanced routing algorithms has created a competitive ecosystem where both centralized and decentralized venues can offer deep liquidity and predictable execution costs.
Economic implications: efficiency, risk, and capital allocation
- Reduced cost of capital for large trades. With lower price impact for sizable orders, institutions can execute large trades with less adverse selection and less market impact. This reduces the true cost of capital for market participants seeking to rebalance portfolios, arbitrate across venues, or deploy strategic allocations in crypto assets.
- Improved price discovery and market efficiency. As more institutions participate directly on-chain, price discovery mechanisms become more transparent and accessible. This can narrow bid-ask spreads over time and enhance the integrity of reference prices used by derivatives, lending markets, and structured products.
- Risk transfer and collateral dynamics. On-chain trading, when coupled with on-chain risk management tools like liquidations, oracle-based pricing, and automated hedging strategies, can improve risk transfer efficiency. Participants can align execution with on-chain collateralization, reducing the need for off-chain intermediaries and the associated counterparty risk.
- Network effects and liquidity migration. The ongoing migration of liquidity across protocols and chains can create network effects where richer liquidity pools attract more participants. This can amplify the robustness of price formation and resilience during periods of volatility, as more capital competes for execution across multiple venues.
Regional landscape and cross-market comparisons
- Solana ecosystem. Solana’s high-throughput architecture has enabled rapid, low-cost trades on-chain. The current competitive costs for large SOL/USDC trades demonstrate the platform’s ability to sustain high liquidity while maintaining tight price impact. Innovations in concentrated liquidity and enhanced order routing have accelerated this trajectory, attracting more institutional activity to Solana-based DEXs.
- Ethereum and layer-2 networks. While the focus here is Solana, Ethereum-based DEXs and layer-2 solutions continue to mature. Layer-2 scaling reduces gas fees and increases throughput, enabling more efficient on-chain execution for large trades. Cross-chain interoperability is crucial for institutions seeking to optimize execution quality across multiple networks.
- Centralized exchanges. Despite the rise of on-chain alternatives, centralized exchanges retain advantages in certain contexts, including extremely deep liquidity during peak trading sessions, sophisticated custodial services, and extensive derivative suites. The observed 5–12 basis point price impacts on major centralized venues for large SOL/USDC trades illustrate that these platforms still offer competitive execution characteristics, especially when liquidity is concentrated.
- Comparative takeaway. The data suggest that top-tier DEXs are narrowing the execution-cost gap with centralized venues, and in some cases surpassing them for specific assets and trade sizes. This dynamic is reshaping how traders allocate their orders and how liquidity providers compete across the on-chain and off-chain spectrum.
Technological drivers behind improved on-chain execution
- Concentrated liquidity and intelligent routing. DEXs increasingly employ concentrated liquidity strategies that mimic the depth of centralized order books. Advanced routing algorithms scan multiple pools and routes simultaneously to minimize slippage, achieving near-optimal execution costs for large trades.
- On-chain order types and native settlement. Custom order types, gas-efficient transaction design, and native settlement within the blockchain reduce settlement latency and counterparty risk. These features contribute to a more efficient trading experience, especially for institutional participants seeking predictable execution timelines.
- Cross-chain interoperability. Bridges and cross-chain protocols enable traders to access multiple liquidity sources without leaving the ecosystem. This breadth of access improves slippage profiles and allows traders to select optimal routes across networks, further enhancing execution quality.
- Data transparency and monitoring. On-chain data transparency allows traders to verify execution quality, liquidity depth, and price impact in real time. This visibility supports more precise risk assessment, compliance, and reporting for regulated entities entering the space.
Public reaction and market sentiment Market participants have reacted to this shift with cautious optimism. Traders appreciating lower costs and better execution quality view on-chain venues as viable complements, or even alternatives, to traditional venues for certain trades. Some institutions remain prudent, seeking robust custody, compliance, and risk controls before committing substantial capital to on-chain execution. The broader sentiment is one of cautious enthusiasm: as markets become more efficient and transparent, liquidity tends to migrate toward venues that offer a favorable combination of cost, speed, and reliability.
Policy and regulatory context Regulatory clarity remains essential for broader institutional adoption. As on-chain trading grows, so does the need for clear frameworks around custody, compliance, and risk management. Regulators are increasingly scrutinizing DeFi protocols and on-chain exchanges to ensure investor protection, market integrity, and robust operational controls. In this environment, operators that emphasize auditability, security, and compliant liquidity provision are better positioned to attract institutional participation.
Conclusion: an evolving, efficient, on-chain trading landscape The rapid decline in DEX execution costs relative to centralized exchanges signals a meaningful evolution in crypto markets. The convergence of on-chain technology, concentrated liquidity, and sophisticated routing is enabling large trades to be executed with minimal price impact on Solana-based DEXs, while centralized venues continue to offer competitive benchmarks. This dual-path growth—where on-chain and off-chain venues increasingly compete on similar terms—points to a more resilient and efficient market structure that benefits a broad spectrum of participants, from individual traders to institutional asset managers.
In this evolving landscape, traders should monitor liquidity depth, routing strategies, and cross-chain opportunities to optimize large-trade executions. As on-chain platforms continue to close the gap with traditional venues, the line between centralized and decentralized trading continues to blur, heralding a more integrated and efficient crypto trading ecosystem.